Introduction
Vertically aligning HTML contents in CSS has always been a herculean task and has been described by many web developers as tricky to implement. However, modern CSS has made available a number of ways to vertically align HTML contents easily. Content alignment has never been easier at this time, and in this article, we'll look at different techniques to vertically align HTML content using CSS.
Steps we'll cover include:
- Vertical alignment using margins
- Vertical alignment with Flexbox
- Vertical alignment using CSS Grid.
- Vertical alignment using table display (display: table)
- Vertical alignment using absolute positioning (position: absolute)
- Vertical alignment using css transforms
- Vertical alignment using line-height
- Vertical alignment using inline display (display: inline) and vertical-align: middle
- Vertical alignment using inline-block display (display: inline-block) and vertical-align: middle
- Vertical Alignment using “before” pseudo-element and vertical-align: middle
Vertical alignment using margins
Margins in CSS are used to generate space around the borders of contents.
Here are examples on how to easily vertically align contents with margins.
Example
Using the CSS property margin:auto, You can vertically and horizontally align HTML contents to the center. However, this is possible only when the following conditions are met:
- The parent element should have a given
height. - The child element should have a specified
height. - The parent element should have either a display of
flexorgrid.
A sample of this can be displayed below:
HTML CODE:
<html>
<body>
<section class="parent-element">
<div class="child-element">The text is here!</div>
</section>
</body>
</html>
CSS CODE:
.parent-element {
display: [flex or grid];
height: 500px;
border: 1px solid #000;
}
.child-element {
margin: auto;
}

Vertical alignment with Flexbox
Flexbox is a CSS3 layout module that aims to simplify the process of designing flexible, responsive layout structures without the need for positioning or float. Unlike some other CSS frameworks, it is orientation agnostic and lets you automatically align and resize containers based on the height and width of the screen.
Here are examples on how to effortlessly vertically align contents with flexbox.
Example 1
With the CSS properties display: flex, align-items: center and justify-content: space-around, we can vertically and horizontally align HTML contents.
HTML CODE:
<html>
<body>
<div class="nav">
<div class="nav-item">Home</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
CSS CODE:
.nav {
display: flex;
justify-content: space-around; /* aligns the items horizontally */
align-items: center; /* aligns the items vertically */
height: 100px;
background-color: #333;
color: #fff;
}

Example 2:
With the CSS properties display: flex, align-items: center and justify-content: center, we can also vertically align HTML contents.
We will update the first example CSS code to show this:
CSS CODE:
.nav {
display: flex;
height: 100px;
background-color: #333;
color: #fff;
justify-content: center; /* aligns the items horizontally */
align-items: center; /* aligns the items vertically */
}
Vertical alignment using CSS Grid.
The CSS Grid Layout Module provides a two dimension grid-based layout system with rows and columns, allowing you to design web pages with ease.
Here are examples on how to effortlessly vertically contents with flexbox.
Example 1:
With the CSS properties display: grid, align-items: center and justify-content: center, we can also vertically align HTML contents.
HTML CODE:
<html>
<body>
<div class="grid">
<div class="item">Centered Item</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
CSS CODE:
.grid {
display: grid;
height: 97vh;
justify-content: center; /* aligns the items horizontally */
align-items: center; /* aligns the items vertically */
border: 1px solid #000;
}
.item {
font-size: 20px;
}
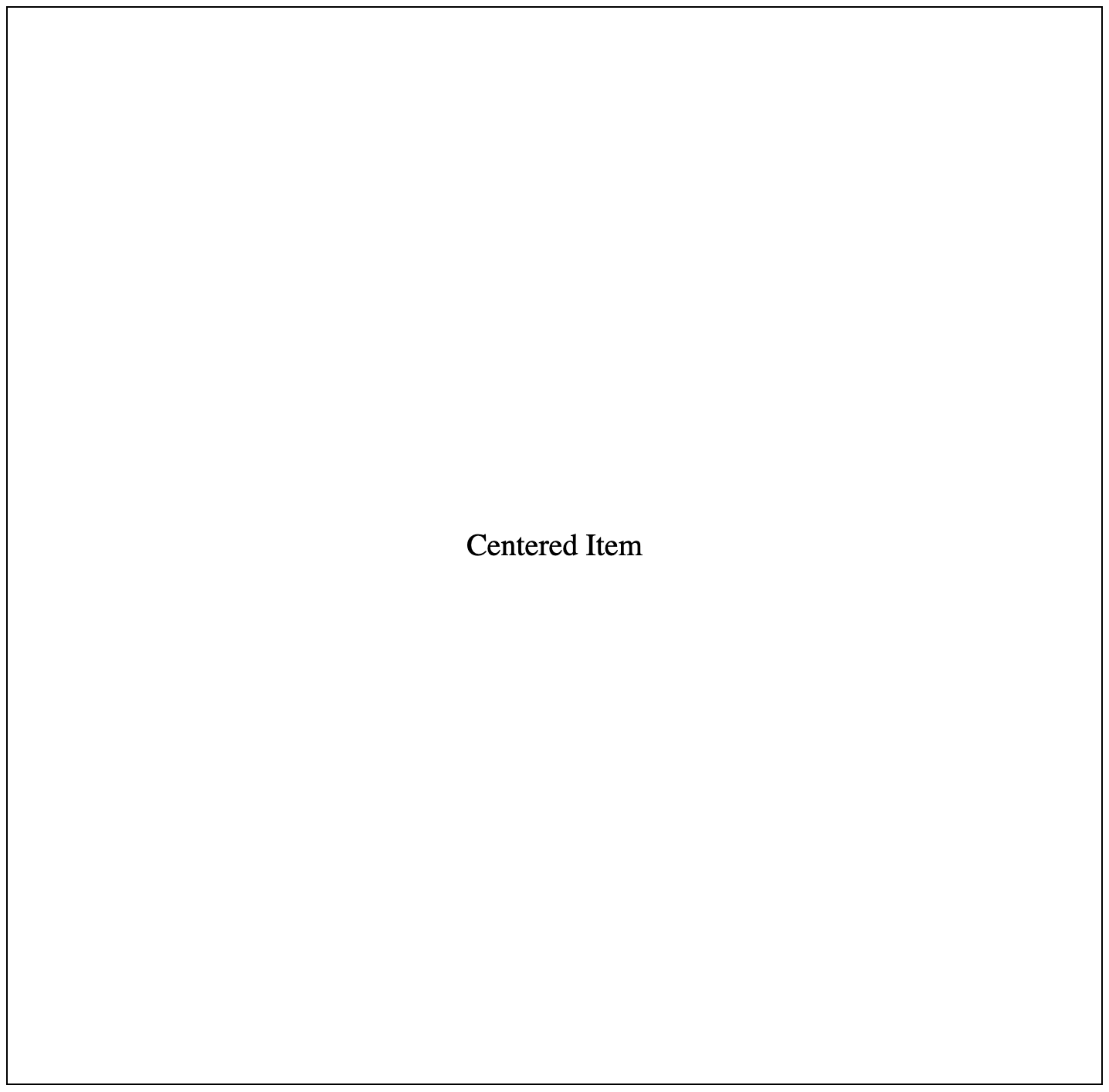
Example 2:
With the CSS properties display: grid, place-items: center (which is a combination of align-items: center and justify-content: center), we can also vertically align HTML contents.
We will update the CSS code of the first example to show this:
CSS CODE:
.grid {
display: grid;
height: 97vh;
place-items: center; /* aligns the items vertically and horizontally */
border: 1px solid #000;
}
.item {
font-size: 20px;
}
Example 3:
With the CSS properties display: grid, align-self: center, we can also vertically align HTML contents.
We will update the CSS code of the first example to show this:
CSS CODE:
.grid {
display: grid;
height: 97vh;
border: 1px solid #000;
}
.item {
align-self: center; /* aligns the items vertically only */
font-size: 20px;
}

Vertical alignment using table display (display: table)
Tables are a common and useful tool for displaying data on websites and web applications. It was the common method of presenting information in rows and columns before to the introduction of modules like flex and grid.
Here are examples on how to vertically align contents with tables.
Example:
Using the CSS property display: table, display: table-cell, vertical-align: middle, You can vertically align contents to the center. However, this is possible only when the following conditions are met:
- The parent element must have the
display: tableproperty. - When the parent element must have a given
height. - The child element must have the
display: table-cellproperty. - The child element must have the
vertical-align: middleproperty.
A sample of this can be displayed below:
HTML CODE:
<html>
<body>
<div class="parent-element">
<div class="child-element">Center text!</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
CSS CODE:
.parent-element {
display: table; /* table display*/
height: 50vh;
width: 100%;
border: 1px solid black;
}
.child-element {
display: table-cell; /* table-cell display*/
vertical-align: middle; /* vertical align*/
text-align: center;
}
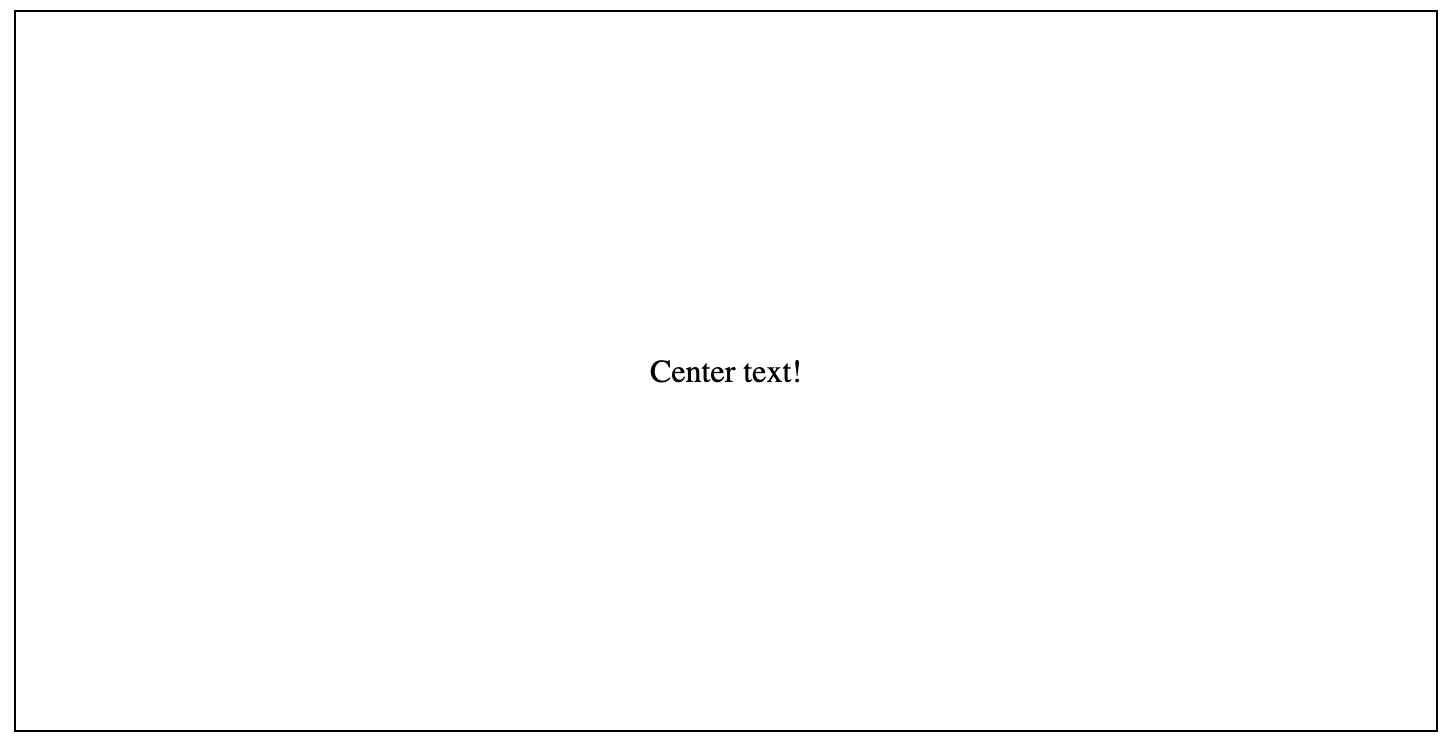
Vertical alignment using absolute positioning (position: absolute)
The position CSS property specify how an element is positioned in a document. Positioned elements' final positioning is determined by their top, right, bottom, and left properties.
We could use these positioning properties to vertically align contents.
Example:
Using the CSS properties position: relative and position; absolute and margin; auto, You can vertically align contents to the center. However, this is possible only when the following conditions are met:
- The parent element must have the
position: relativeproperty. This is to ensure that the positioning of the element occurs solely within the parent container and does not extend outside it. - The parent element should have a specified
height. - The child element must have the
position: absoluteproperty - The child element should have the positioned properties:
top: 0;bottom: 0;left: 0;right: 0; - The child element should have a specified
heightas well.
HTML CODE:
<html>
<body>
<div class="parent-element">
<div class="child-element">Center text!</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
CSS CODE:
.parent-element {
position: relative;
height: 50vh;
border: 1px solid black;
}
.child-element {
position: absolute;
top: 0;
bottom: 0;
left: 0;
right: 0;
margin: auto;
height: 20px; /* requires explicit height*/
border: 1px solid black;
text-align: center;
}

Vertical alignment using css transforms
The translate() CSS property repositions an element in both horizontal and vertical directions.
We will give examples on how to use the translate property.
Example 1
Using the CSS properties position: relative and position; absolute and transform: translate(-50%, -50%), You can vertically and horizontally align contents to the center. This has been a popular way to vertically align contents. However this is possible only when the following conditions are met:
- The parent element must have the
position: relativeproperty. - The parent element should have a specified
height. - The child element must have the
position: absoluteproperty. - The child element should have the positioned properties:
top: 50%;left: 50%;. - The child element should have the translate property:
transform: translate(-50%, -50%);. This property repositions the child element to fit into the center of the parent element.
HTML CODE:
<html>
<body>
<div class="parent-element">
<div class="child-element">Center text!</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
CSS CODE:
.parent-element {
position: relative;
height: 50vh;
border: 1px solid black;
}
.child-element {
position: absolute;
top: 50%;
left: 50%;
transform: translate(-50%, -50%);
}

Example 2
We can vertically align items only using the CSS properties position: relative and position; absolute and transform: translateY(-50%),
We will update the CSS code of the first example to show this:
CSS CODE:
.parent-element {
position: relative;
height: 50vh;
border: 1px solid black;
}
.child-element {
position: absolute;
top: 50%;
transform: translateY(-50%);
}

Vertical alignment using line-height
The line-height CSS property specifies the height of a line box. It's widely used to specify the spacing between lines of text. On block-level elements, it sets the minimum height of line boxes within them. On non-replaced inline items, it defines the height used to compute the line box height.
We will give examples on how to use the line-height property to vertically align contents.
Example:
Using the CSS properties line-height: [lineheight value] and height: [height value], You can vertically align HTML contents to the center. However this is possible only when the following conditions are met:
- The parent element should have a specified
height. - The child element must have the
line-heightproperty. - The
heightof the parent element must be equal to theline-heightof the child element.
HTML CODE:
<html>
<body>
<div class="parent-element">
<div class="child-element">Center text!</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
CSS CODE:
.parent-element {
height: 100px;
background-color: #333;
}
.child-element {
line-height: 100px;
padding: 0 10px;
color: #fff;
text-decoration: none;
text-align: center;
}

Vertical alignment using inline display (display: inline) and vertical-align: middle
The CSS's vertical-align attribute specifies how elements on a line are aligned. This property works to aligning inline elements only (and not block elements).
Example:
In this example, with the inline display and the vertical-align property, You can vertically align contents to the center. However this is possible only when the following conditions are met:
- The parent element should have a specified
line-height. We do this to increase the line box so that thevertical-alignproperty uses to align the contents in the middle of that line-box. - The child element must have the
vertical-alignproperty.
HTML CODE:
<html>
<body>
<div>
<a href="#">Some link</a>
<span>Some text</span>
</div>
</body>
</html>
CSS CODE:
div {
background: #fff;
margin: 10px;
line-height: 200px;
border: 1px solid #000;
}
div > * {
vertical-align: middle;
line-height: normal;
}
a {
background-color: red;
color: white;
height: 20px;
border: solid 1px #666;
padding: 5px;
}
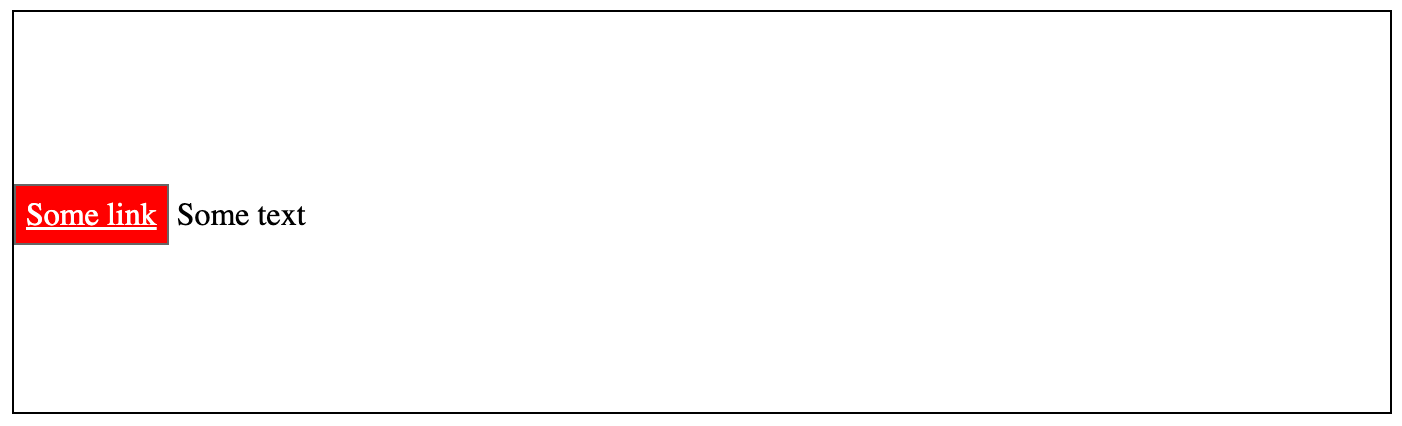
Vertical alignment using inline-block display (display: inline-block) and vertical-align: middle
In this example, with the inline-block display and the vertical-align property, You can vertically align contents to the center.
Example:
HTML CODE:
<html>
<body>
<div class="parent-element">
vertical align middle:
<div class="child-element"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
CSS CODE:
.parent-element {
padding: 30px 10px;
border: 1px solid;
}
.child-element {
vertical-align: middle;
display: inline-block;
background: fuchsia;
width: 30px;
height: 30px;
border-radius: 50%;
}
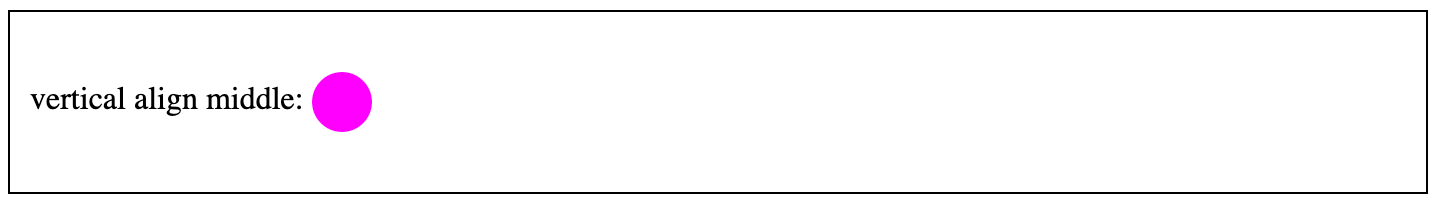
Vertical Alignment using “before” pseudo-element and vertical-align: middle
This type of alignment is usually called the ghost element alignment. This alignment employs using the inline-block display property on a ghost (pseudo) element of the parent element, inherits the parent's element full height, then sets the vertical-align: middle property for both thepseudo-element of the parent element and the child element.
Example:
HTML CODE:
<html>
<body>
<div class="parent-element">
<p>Child of parent element with pseudo ghost element</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>
CSS CODE:
.parent-element {
background: #fff;
width: 240px;
height: 200px;
margin: 15px;
color: #fff;
resize: vertical;
overflow: auto;
padding: 20px;
border: 1px solid #000;
position: relative;
}
.parent-element::before {
content: " ";
display: inline-block;
height: 100%;
width: 1%;
vertical-align: middle;
}
.parent-element p {
display: inline-block;
vertical-align: middle;
width: 190px;
margin: 0;
padding: 10px;
background: #83d483;
}
Conclusion
In this article, we examined some CSS techniques for vertical alignment of contents. Using these techniques will make it easy to align contents vertically on your webpages or web applications.

