Introduction
Changing Node.js versions was always difficult for developers. Due to version compatibility, changing Node.js versions for the current session was common but tedious. The end of 2023 release of Node version manager solves this problem. This article shows how to use NVM to check and modify Node.js version. We'll explain how to install and use NVM to swap Node.js versions. Let's understand what is an NVM and how it boosts developer productivity.
Steps we'll cover:
- What is Node Version Manager (NVM)?
- Why Developers Need NVM
- Preparing for NVM Installation
- Installing NVM
- Possible Errors and Edge Cases
- Installing and Managing Node.js Versions with NVM
- Listing All Available Node.js Versions
- How do I change Node.js Versions
What is Node Version Manager (NVM)?
- Definition: NVM is a multi-functional command-line utility. It is designed to make it easy to work with multiple Node.js versions on one machine.
- Primary Function: NVM’s primary functionality is to add the ability to install any version of Node.js, giving quick access to it via the command line. Often different projects require different versions for compatibility, and NVM enables developers to switch between the node versions effortlessly.
- Benefits of Using NVM:
- Simplicity: No manual system environment variable modifications. NVM makes transitioning between node versions easy.
- Isolation: Each Node.js version runs independently, therefore its global npm packages are unique. This isolation prevents version conflicts.
- Flexibility: NVM lets you swiftly transition between Node.js versions, making it easier to manage projects with different versions.
Why Developers Need NVM
- Multiple Node.js Versions: Software developers often work on multiple projects that require different versions. Developers can swap versions effortlessly with NVM.
- Problems Solved by NVM:
- Without NVM, developers may need to uninstall and reinstall Node.js to switch versions. NVM manages and switches between versions with one command, eliminating this complication.
- Developers may use virtual machines or dual boot to work with different Node.js versions. NVM manages many Node.js versions on one OS, eliminating this.
Of course, it is also possible to install different versions of Node.js without using NVM and you can also switch different versions without NVM. However, it will require frequent modification to PATH variable to point to the directory of a specific Node.js version. However, using NVM gives the flexibility to switch Node.js versions with a simple command.
Preparing for NVM Installation
Prerequisites for Installing NVM
- Command Line Access: NVM is a command-line tool. Therefore, you need to have access to a terminal. On macOS and Linux, you can use the built-in terminal. On Windows, you can use PowerShell or Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL).
- cURL or Wget: These are tools that you can use to download NVM. Most Unix-like operating systems come with these tools pre-installed. If not, you can install them using your package manager (like
aptfor Ubuntu,brewfor macOS, etc.). - Scripting Runtime: NVM installation script is written in bash. You need to have
bash,zsh,ksh, ordashas your shell. If you’re using Windows, you can use WSL which provides a Linux-compatible shell environment.
Compatibility of NVM with Different Operating Systems
- macOS and Linux: NVM is fully compatible with macOS and Linux. It’s a bash script, and it works well with the Unix-like environment provided by these operating systems.
- Windows: NVM does not officially support Windows. However, there’s a separate version called “nvm-windows” that provides similar functionality. Alternatively, you can use WSL on Windows to get a Linux-like environment where you can run the standard NVM.
- BSDs and Other Unix-like OS: While not officially stated, NVM should work on any Unix-like operating system that has a POSIX-compliant shell and the necessary tools (
curlorwget,tar, etc.). However, the compatibility might not be as robust as macOS and Linux.
Installing NVM
Step-by-Step Instructions
- Open a Terminal Window: Launch your terminal application. This could be Terminal on macOS, Command Prompt or PowerShell on Windows, or your preferred terminal emulator on Linux.
- Download the NVM Installation Script: NVM is installed by running a script in your terminal. The script is available on the NVM GitHub repository. Use
curlorwgetto download the script. Here’s the command usingcurl:
curl -o- https://raw.githubusercontent.com/nvm-sh/nvm/v0.39.7/install.sh | bash
Or you use wget:
wget -qO- https://raw.githubusercontent.com/nvm-sh/nvm/v0.39.7/install.sh | bash
If you do not wish to use either wget or curl, you can also download the script from here and then install the script.
Here is what you will see if you execute the above curl command:
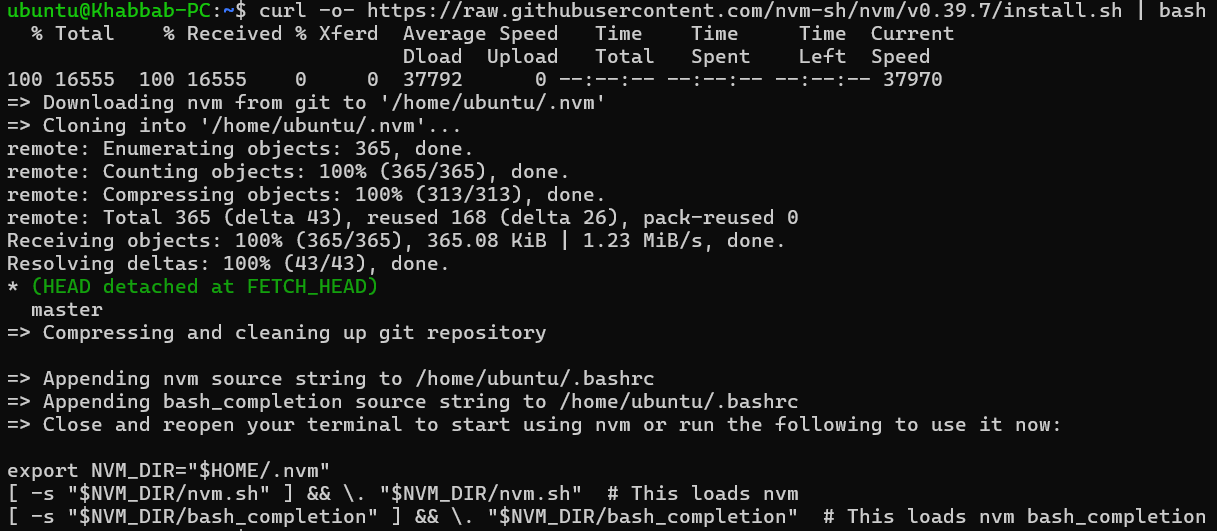
- Run the NVM Installation Script: The
wgetorcurlcommand downloads the script and runs it in one go. The script clones the NVM repository to~/.nvm, and adds the source lines to your profile (~/.bash_profile,~/.zshrc,~/.profile, or~/.bashrc). - Verify the Installation: Close your terminal and open a new one. Verify that NVM is installed and working with the following command:
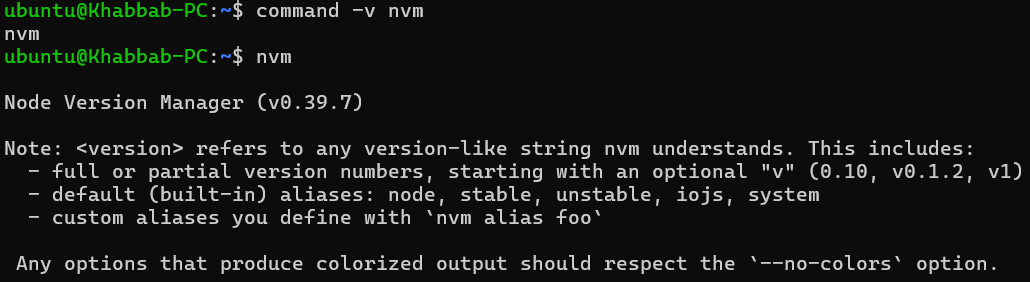
command -v nvm
This command should output nvm, indicating that NVM is installed and accessible. You can also run the command nvm to see the version of nvm and its usage details.
Possible Errors and Edge Cases
Command Not Found: If the terminal says
command not foundafter runningcommand -v nvm, this means that the terminal can’t find thenvmcommand. You may need to close and reopen your terminal or restart your computer. Below screenshot confirms this scenario. Closing and re-launching the terminal solves this issue though.
No Curl or Wget: If your machine doesn’t have
curlorwget, you’ll need to install one of them to download the NVM installation script.Windows Users: The above instructions are for Unix-based systems like Linux and macOS. If you’re on Windows, consider using a version of NVM made for Windows, or use Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL).
Installing and Managing Node.js Versions with NVM
Installing Latest Version
You can install the latest version of Node.js using NVM without knowing the exact version number. NVM provides a special command for this purpose. Here’s how you can do it:
nvm install node
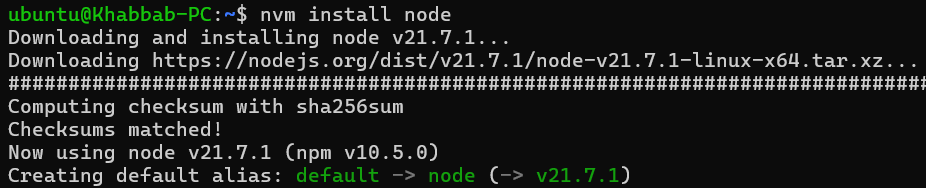
The nvm install node command will fetch the latest version of Node.js and install it. For example, the latest version is 21.7.1. After the installation, the latest version will automatically become the active version in your current terminal session, this is evident from the last line in above screenshot where nvm is setting the installed Node.js version as default Node.js version.
Installing a Specific Node.js Version
To install a specific version of Node.js, use the nvm install command followed by the version number. For instance, to install Node.js version 14.15.1, you would use the following command:
nvm install 14.15.1
The nvm install command downloads the specified version of Node.js and npm, allowing you to use them immediately.
Listing All Available Node.js Versions
NVM provides a straightforward way to view all installed Node.js versions. The nvm ls command displays a list of installed versions, with the current version highlighted:
nvm ls
After installing the latest version of Node.js (which is 21.7.1 as of writing this), this is what the above command shows:
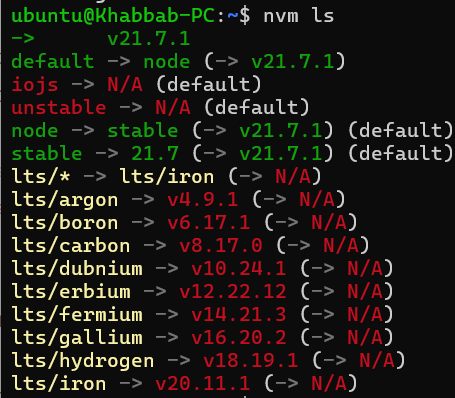
Looking at the above screenshot, the terms “stable”, “default”, and “current” have specific meanings:
- Stable: This refers to the latest stable version of Node.js that has been released and deemed reliable for use. Stable versions have undergone testing and are considered free of known critical bugs. This may or may not be your current or default version.
- Default: This is the version of Node.js that your system will default to when you open a new terminal session. If you’ve set a default version in NVM, that version will be automatically used. Otherwise, the system’s default Node.js installation will be used.
- Current: This term is used to indicate the version of Node.js that is currently active in your terminal session. This could be different from the default version if you’ve used
nvm useto switch to a different version. You can identify this version by-->sign in the above screenshot.
In above screenshot, the version 21.7.1 is the current version as well as default and stable version. After installing 14.15.1, it will become the current version instead of 21.7.1, however 21.7.1 will remain as default. See below screenshot after running the nvm ls command after installing version 14.15.1 on top of 21.7.1.
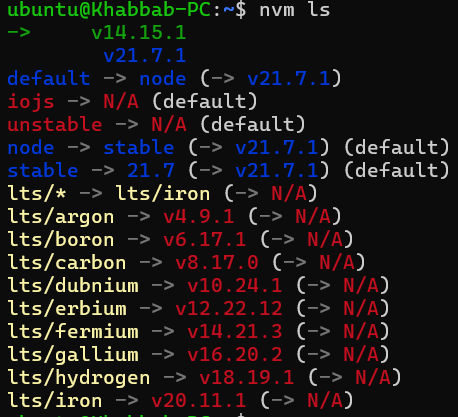
In above screenshot, 14.15.1 is current version, but stable and default versions are still 21.7.1. If another stable version 21.7.2 is released tomorrow, then 21.7.2 will be shown as stable version and 21.7.1 will be shown as default version.
To view all available versions for installation, use the nvm ls-remote command:
nvm ls-remote
This command fetches and displays a list of all Node.js versions available for installation.
How do I change Node.js Versions
Changing Node.js versions is as simple as using the nvm use command followed by the version number. For example, to switch to Node.js version 21.7.1, you would use:
nvm use 21.7.1
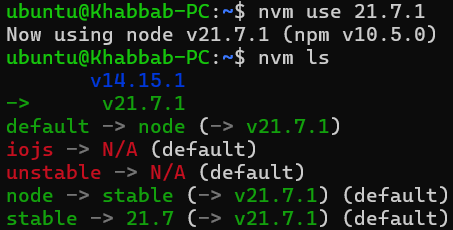
This command makes the specified version the active Node.js version in your current terminal session. If you close the terminal, the effect of above command will be nullified and default version of Node.js will become active.
How do I revert to an older version of node?
You can use the same command nvm use <older-version-number> to revert to an older version for this session. For example, nvm use 14.5.1will revert your current Node.js version to 14.5.1 which is much older version. That older version will of course need to be installed first.
The NVM manager is intelligent enough to use the correct Node.js version even if you use just the prefix of the version number. For example:
nvm use 14will work asnvm use 14.5.1as there is only one installed version that started with 14nvm use 21will work asnvm use 21.7.1as there is only one installed version that started with 21
If you want to use a version as current version even after closing a terminal, you can change your default version by using the below command nvm alias default 14.5.1 where you can replace 14.5.1 with any Node.js version you want to be default.
Verify the current version
In above screenshots, you noticed that the current version of Node.js is shown by --> in the output of command nvm ls. Another way to verify the current version of Node.js using NVM with the nvm current command. This command will display the version of Node.js that is currently in use in your terminal session. Here’s how you can use it:
nvm current
This command will output the version of Node.js that is currently active. For example, it might output v14.15.1 if that’s the version you’re currently using. If no version is active, it will output system, indicating that the system’s default Node.js installation is currently in use.
Conclusion
If you have read this article, you are now expert in using NVM to change your Node.js version. Using a version manager like NVM improves the efficiency of developers and simplify the development process. Using NVM, not only you can specify any Node.js version for your current session, but you can also modify the system's default Node.js version as well.